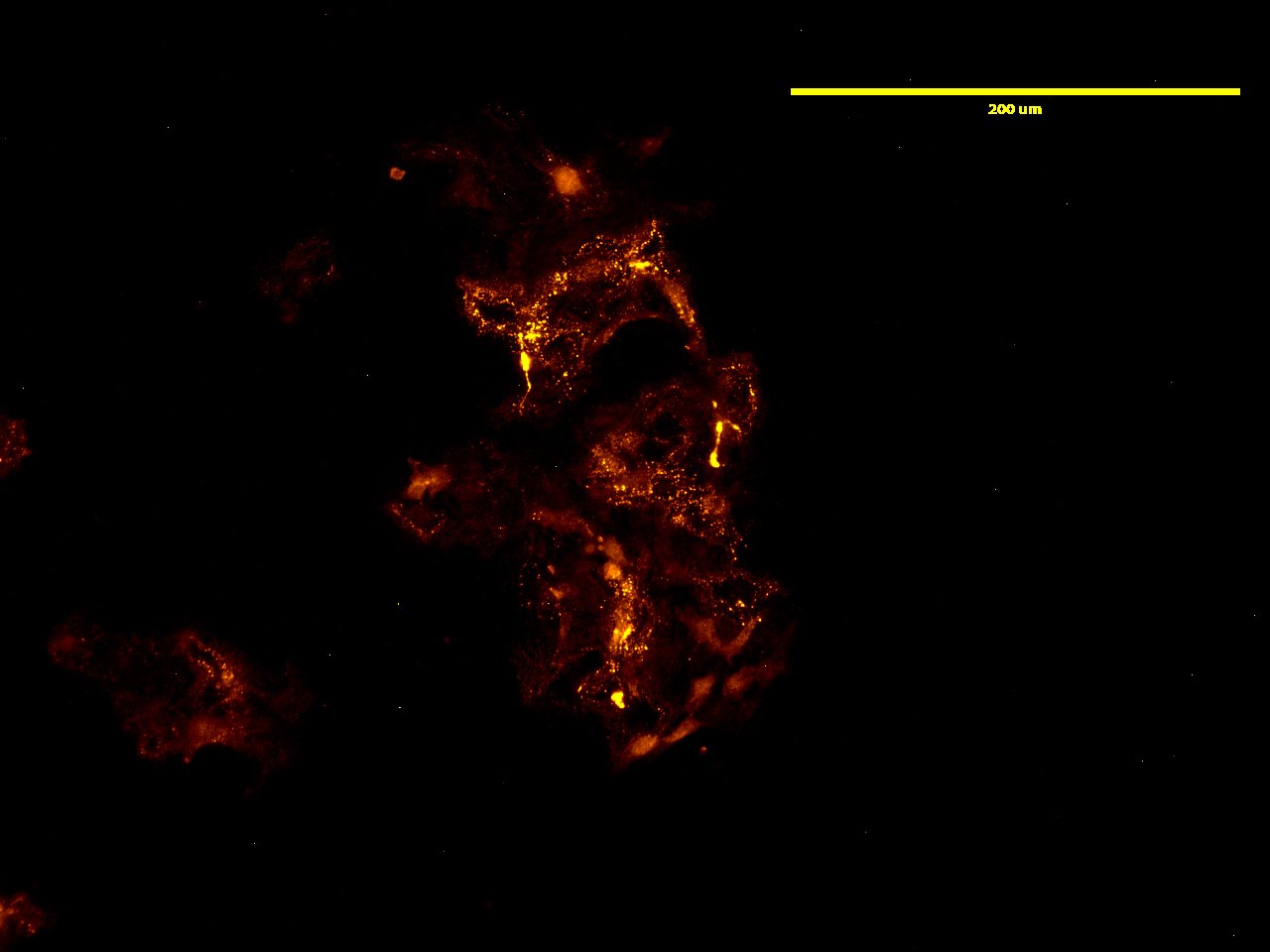
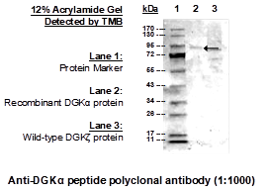
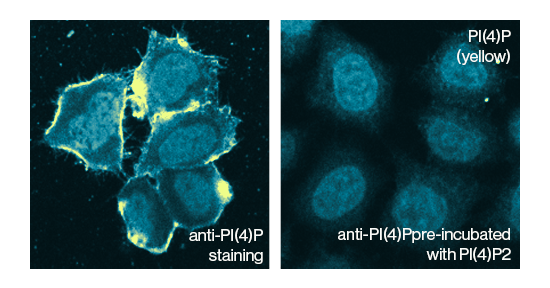
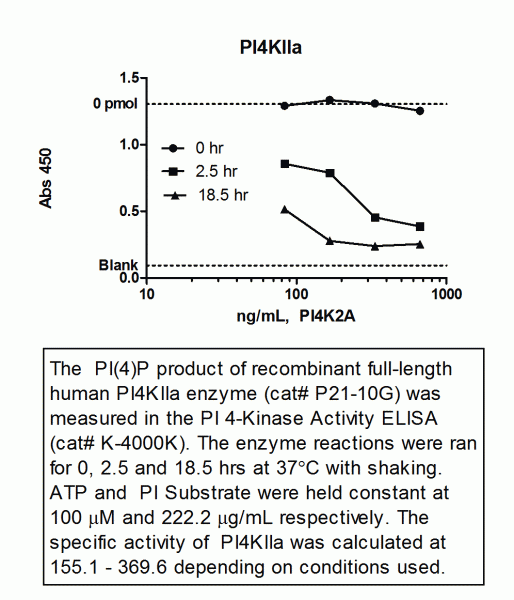
Hyaluronic Acid or hyaluronan (HA) is a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a homogenous non-branching polymer made from a non-sulfated repeating disaccharide. It is known to have a specific set of hyaluronic acid binding proteins (HABP) that can be used like antibodies for detection of HA in in vitro applications, including cell staining.
Versican is one of the many HABP that belong to the link module superfamily. Versican binds hyaluronan through the specific binding domain called “link module”, in which, it contains an immunoglobulin domain and two contiguous link modules. Echelon’s Biotinylated Versican G1 Domain (biotin VG1) contains only the biotinlyated G1 domain from versican. G-HA02 has been validated for use in detecting hyaluronic acid (HA) via ELISA and ICC.
Publications
1. Rivas F, Zahid OK, Reesink HL, Peal BT, Nixon AJ, DeAngelis PL, et al. Label-free analysis of physiological hyaluronan size distribution with a solid-state nanopore sensor. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1037.
2. Yuan, H., R. Amin, et al. (2015). Determination of hyaluronan molecular mass distribution in human breast milk. Analytical Biochemistry 474: 78-88.