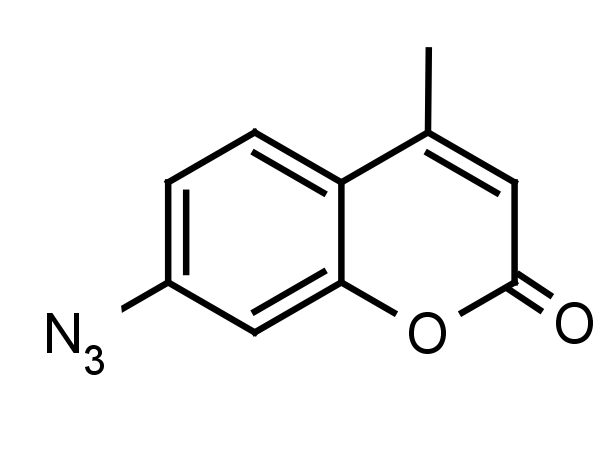
This novel and selective probe for hydrogen sulfide (H2S), 7-azido-4-methylcoumarin (AzMC), is useful for monitoring cystathionine B-synthase (CBS) catalyzed reactions, which play a critical role in human sulfur metabolism. Deactivated CBS is characterized by high plasma levels of homocysteine and H2S, resulting in clinical manifestations of numerous disease states. AzMC, used as a fluorgenic probe and concurrent CBS activity, can be used to select compounds for activation or inhibition of this enzyme, and is suitable for high-throughput screening and the development of potential therapeutics. In addition, AzMC has been used as a photoaffinitry probe for the substrate binding site of human phenol sulfotransferase (SULT1A-1 or P-PST-1).
Featured in References
1. M.K. Thorson, T. Majtan, J.P. Kraus, A.M. Barrios “Identification of Cystathionine β-Synthase Inhibitors Using a Hydrogen Sulfide Selective Probe.” Angewandte Chemie (Int. ed. Eng.) 2013, 52, 4641-4144. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201300841
2. G. Chen, et al. “Photoaffinity labeling probe for the substrate binding site of human phenol sulfotransferase (SULT1A1): 7-azido-4-methylcoumarin.” Protein Sci., 1999, 8, 2151-2157, doi:10.1110/ps.8.10.2151
3. Q-L Xie, et a. “An azidocoumarin-based fluorescent probe for imaging lysosomal hydrogen sulfide in living cells” Analytical Methods, 2017, DOI: 10.1039/C7AY00862G
Bulk discounts available, please email echelon@echelon-inc.com for information.