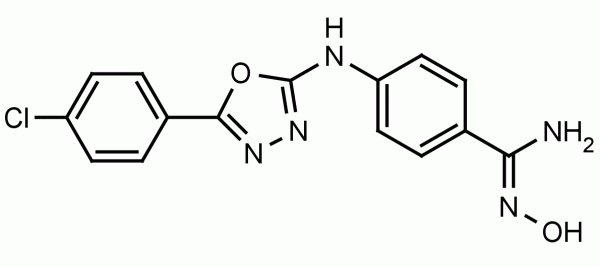
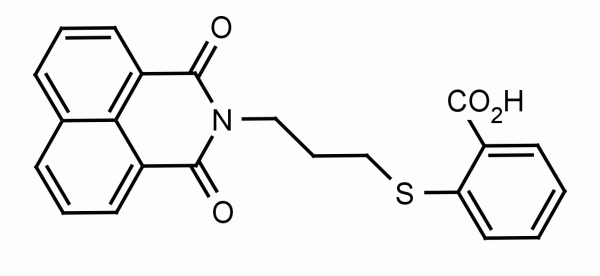
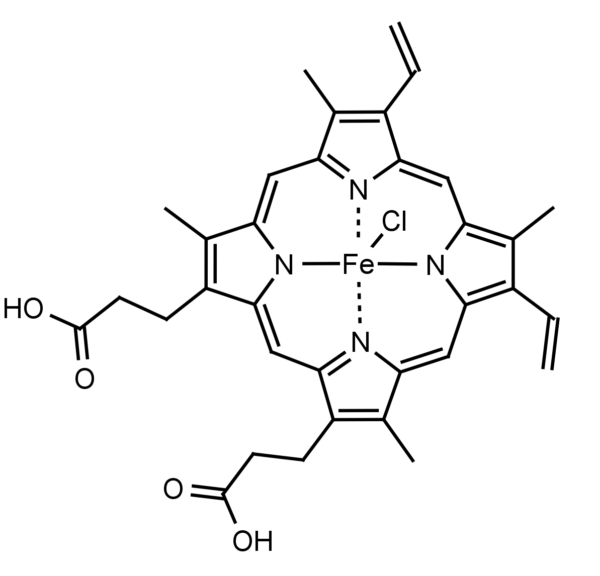
Hemin induces the activity of the enzyme heme-oxygenase. Heme oxygenase catalyzes the conversion of heme to biliverdin, CO and Fe+3. The induction of heme oxygenase activity has been associated with reduced free radical formation and inflammation, vascular repair, and implicated in tumor growth and metastasis. Hemin has been shown to be effective at 75 μmol/kg in mice or 5 μM for cells in culture.
References
1) Shibahara, S., T. Yoshida, et al. (1978). “Induction of heme oxygenase by hemin in cultured pig alveolar macrophages.” Arch Biochem Biophys 188(2): 243-50.
2) Abraham, N. G. and A. Kappas (2005). “Heme oxygenase and the cardiovascular-renal system.” Free Radic Biol Med 39(1): 1-25.
3) Jozkowicz, A., H. Was, et al. (2007). “Heme oxygenase-1 in tumors: is it a false friend?” Antioxid Redox Signal 9(12): 2099-117.
4) Xia, Z. W., W. W. Zhong, et al. (2006). “Heme oxygenase-1-mediated CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells suppress allergic airway inflammation.” J Immunol 177(9): 5936-45.>
5) Kim, D. H., A. P. Burgess, et al. (2008). “Heme oxygenase-mediated increases in adiponectin decrease fat content and inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in Zucker rats and reduce adipogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells.” J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325(3): 833-40.
6) Basireddy, M., J. T. Lindsay, et al. (2006). “Epithelial cell polarity and hypoxia influence heme oxygenase-1 expression by heme in renal epithelial cells.” Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291(4): F790-5.
![Benzo[a]pyrene - Echelon Biosciences](https://www.echelon-inc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/1452.gif)