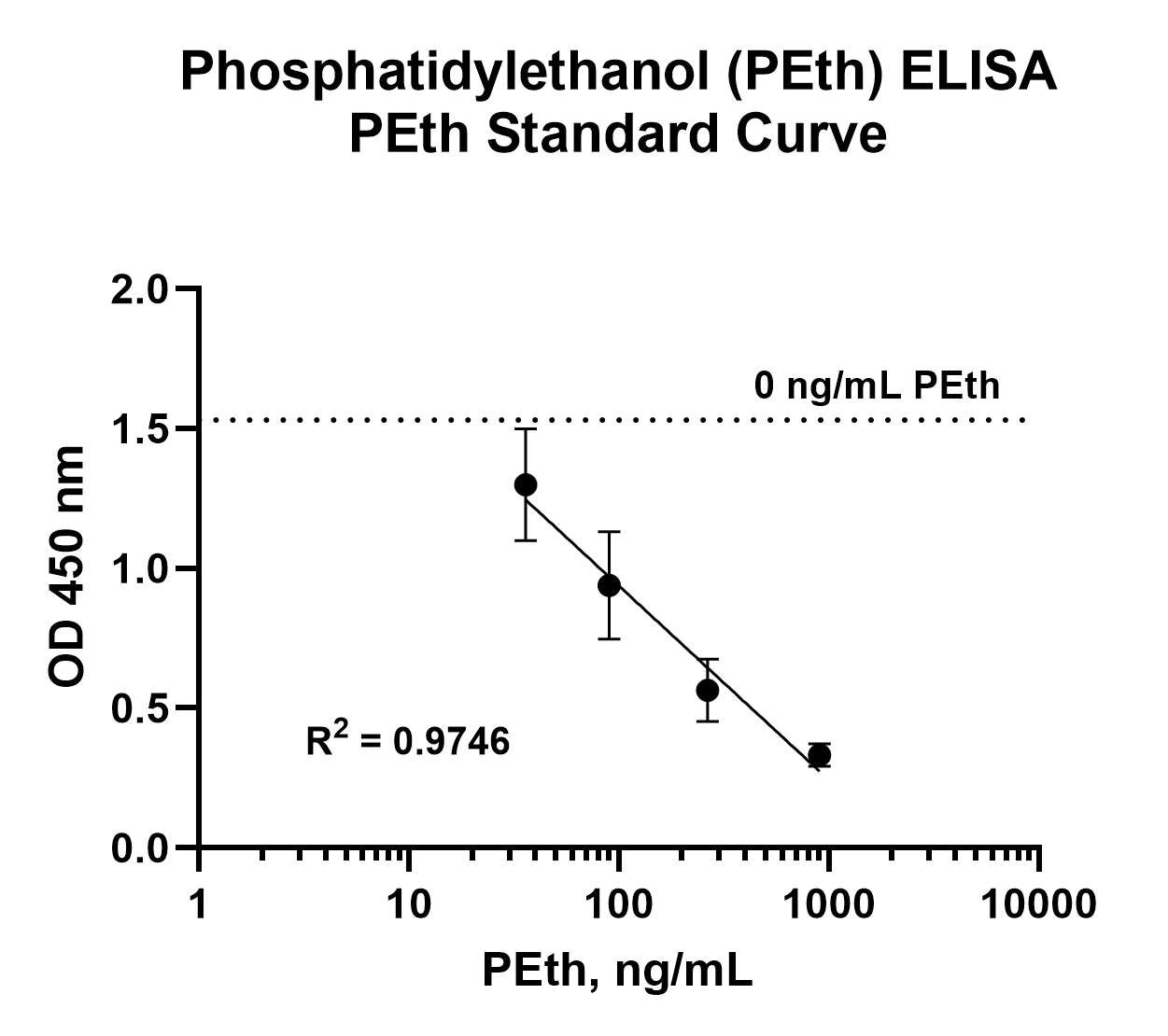
The Phosphatidylethanol (PEth) ELISA detects PEth, an alcohol biomarker, that has been extracted from dried blood spot (DBS) cards.
- 50 µL of whole blood is required for duplicate data points.
- Detects PEth from whole blood spotted on a DBS (dried bloodspot) card.
- Utilizes known PEth containing samples, analyzed by mass spectrometry, as the standard curve for semi-quantitative measurement of PEth.
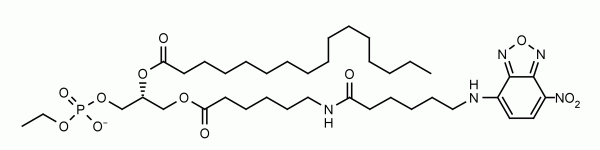
The Phosphatidylethanol (PEth) ELISA assay is a competitive immunoassay. PEth, in a sample extract, competes with PEth on a plate for binding to a PEth specific HRP-conjugated antibody. Therefore, the assay signal is inversely proportional to the amount of PEth present in the sample. This assay is designed for dried blood spot card samples and uses 4 small 3.2 mm (1/8 inch) punches for running duplicate or triplicate measurements. All major PEth molecular species are recognized by the antibody. The assay provides researchers a quick and robust method to screen for PEth in whole blood spotted DBS cards.
PEth is a direct biomarker of alcohol ingestion. It is formed in the blood only when ethanol has been consumed. It is specific and can report previous alcohol consumption beginning a few hours after a drinking event and continuing 2-3 weeks later. Sensitive detection by mass spectrometry using whole blood or dried blood spot (DBS) cards is becoming generally accepted as the gold-standard for detecting past alcohol consumption. The Echelon PEth ELISA is the first commercially available immunoassay for detection of PEth in blood.