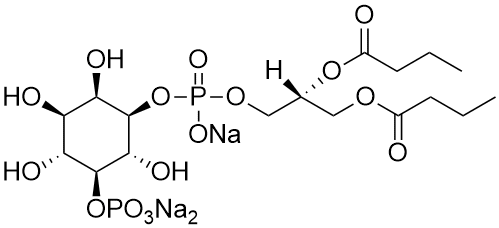
Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate diC4 (PI(5)P diC4) is a synthetic, purified dibutanoyl PI(5)P.
Phosphoinositides (PIPns) are minor components of cellular membranes but are integral signaling molecules for cellular communication. Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate (PI(5)P) is a rare lipid found in the nucleus that can bind the PHD finger of the nuclear adapter protein ING2. PI(5)P is phosphorylated to PI(4,5)P2 by Type II PIP kinases.
Alternate Names: D-myo-Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, Dibutanoyl Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, PtdIns(5)P C4, PI(5)P C4, or PI5P
Bulk discounts available, please email echelon@echelon-inc.com for information.
Publications
1) Guo, J., M. R. Wenk, et al. (2003). “Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIalpha is responsible for the phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity associated with synaptic vesicles.” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(7): 3995-4000.
2) Pendaries, C., H. Tronchere, et al. (2006). “PtdIns5P activates the host cell PI3-kinase/Akt pathway during Shigella flexneri infection.” Embo J 25(5): 1024-34.
3) Ramel, D., F. Lagarrigue, et al. (2011). “Shigella flexneri Infection Generates the Lipid PI5P to Alter Endocytosis and Prevent Termination of EGFR Signaling.” Sci. Signal. 4(191): ra61-.
4) Boal, F. d. r., A. Puhar, et al. (2016). “PI5P Triggers ICAM-1 Degradation in Shigella Infected Cells, Thus Dampening Immune Cell Recruitment.” Cell Reports., doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.079