In this blog post, we will present the specificity data for the Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) Assay Kit II (cat# K-2800S). This ELISA assay, developed in collaboration with Lpath, the original antibody developer, and validated by our customers, will be examined for its specificity against other similar or abundant lipids like Phosphatidic Acid (PA) and Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), and we will demonstrate how it differentiates between various LPA species.
Echelon’s ELISAs focus on biologically significant lipids, which pose unique challenges in assay development. Lipids are notoriously difficult to work with due to their poor solubility and tendency to adhere to tubes and vials. The complexity of detecting lipids is further increased by the potential for cross-reactants and interference from various sample sources. This is where Echelon stands out. With decades of expertise in lipid research and ELISA development, we leverage our knowledge in each assay we create.
Important players in the LPA Assay
Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA)
LPA is a serum-derived bioactive phospholipid involved in diverse cellular processes such as cell proliferation, chemotaxis, platelet aggregation, wound healing, angiogenesis, tumor invasion, and smooth muscle contraction. Recent research suggests that LPA could play a crucial role in cancer development and might serve as a useful biomarker for ovarian cancer. LPA levels are notably higher in women with endometrioid ovarian cancer, according to a pilot study utilizing the LPA Assay. Measuring LPA in vaginal secretions could potentially provide a noninvasive method for diagnosing endometrioid ovarian cancer in post-menopausal women.
Lysophosphatidic (LPA) Antibody
The LPA Antibody (504B3/B3) is a novel monoclonal antibody specifically developed to target LPA. Originally patented and developed by Lpath, the LPA antibody was designed to inhibit the effects of LPA both in vitro and in vivo. As detailed in this blog, the LPA antibody exhibits specificity in competitive ELISA assays. A study using Kinetic Exclusion Assays (KinExA) confirmed that the LPA antibody binds with high affinity to all relevant LPA species, especially 16:0 and 18:2 LPA. Furthermore, they showed that the LPA antibody reduces lesion volume and diffusion following traumatic brain injury, indicating its potential for neutralizing the inflammatory lipid LPA and supporting its use as an LPA-targeted therapeutic.
Lysophosphatidic (LPA) Assay
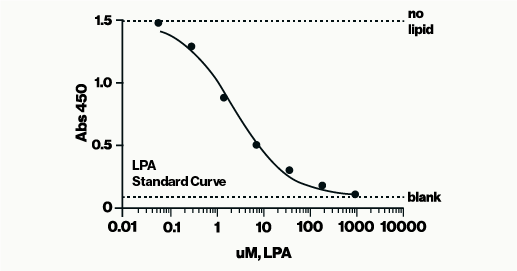
The LPA Assay is a competitive ELISA designed to measure LPA levels in complex samples such as serum, plasma, and tissue homogenates. Also known as an inhibition assay, a competitive ELISA determines analyte concentration by assessing how it interferes with the assay signal. This format is particularly effective for detecting small analytes like lipids in complex mixtures, including plasma, serum, or cell extracts, with minimal sample processing. Competitive ELISAs are less sensitive to sample dilution and matrix effects, and typically show low variation between assays, making them a preferred choice for many of our ELISA assays.
In this assay, samples containing LPA are incubated with LPA antibody in a sample diluent. The resulting mixtures are then applied to an LPA-coated detection plate for competitive binding. Detection is carried out using HRP and colorimetric methods to measure the amount of LPA antibody bound to the plate. LPA concentration is determined using a standard curve of known LPA amounts. The assay is read at 450 nm and takes approximately 3 hours to complete. The complete protocol can be found here.
How specific is the LPA Assay for the different LPA acyl chains?
LPA can differ in length and saturation of their acyl chains. These differences can include the number of carbons in the chain (16-, 18-, or 20-) and whether the fatty acid is saturated or unsaturated. For example, 16:0 and 18:0 are saturated fatty acids, while 16:1, 18:1, 18:2, and 20:4 are unsaturated fatty acids. The most common LPA species in human serum are 18:1-LPA (oleic acid), 18:2-LPA (linoleic acid), and 20:4-LPA (arachidonic acid). According to two publications (Murph2007 & Sutphen2004) LPA is present in human plasma at this ratio C16:0 : C18:0 : C18:1 : C18:2 : C20:4 = 2.8:1.0:1.5:2.6:3.0. Based on these data, we tested a “Mixed LPA” and each LPA independently as shown in Table 1 below. For this experiment, we ran full competitive curves and compared through IC50 values.
| LPA | IC50 (uM) | Ratio to C18:3 IC50 |
| LPA C18:3 | 0.64 | 1 |
| LPA C16:0 | 94.33 | 148 |
| LPA C18:0 | 295.70 | 463 |
| LPA C18:1 | 29.57 | 46 |
| LPA C18:2 | 1.33 | 2 |
| LPA C20:4 | 10.80 | 17 |
| Mixed LPA | 1.75 | 3 |
LPA acyl chain specificity results are summarized below:
- The LPA Assay utilizes LPA C18:3 as the assay standard
- The LPA Assay recognizes the following LPA species (order in high to low): C18:3 > C18:2 > mixed LPA > C20:4 > C18:1 > C16:0 > C18:0.
- Mixed LPA = species of LPA present in human plasma (C16:0 : C18:0 : C18:1 : C18:2 : C20:4 = 2.8:1.0:1.5:2.6:3.0).
How specific is the LPA Assay against other lipids?
An early publication describes a competitive assay utilizing the LPA antibody. Their competitive ELISA is specific for LPA and did not bind the other lipids tested (table 1 in the publication). Their result mirrors our internal testing and aligns with findings from Lpath using comparable competitive ELISA methods.
Table 2 below presents a panel of lipids tested in our LPA Assay at 200 μM against the assay standard LPA 18:3. Results indicate minimal to no cross-reactivity. In addition to the published data and our tested lipids, Lpath's broader panel of lipids tested (not shown) showed similar minimal cross-reactivity. Essentially, when used in a competitive ELISA format, the LPA antibody exhibits high specificity towards its target lipid, LPA.
| Tested Lipid | EBI Catalog # | Detected (uM) | % cross reactivity |
| S1P | S-2000 | 0.04 | 0% |
| Sph | S-1000 | 0.18 | 0% |
| SPC | 0.08 | 0% | |
| LPC 18:0 | L-1518 | 0.04 | 0% |
| PS 16:0 | L-3116 | 0.13 | 0% |
| PC 16:0 | L-1116 | 0.13 | 0% |
| PG 16:0 | 0.01 | 0% | |
| PA 16:0 | L-4116 | <0 | 0% |
| PE 16:0 | L-2182 | 0.17 | 0% |
| Lyso PAF | 0.04 | 0% | |
| Brp-LPA | L-7416 | 0.08 | 0% |
| DAG | L-0016 | 0.05 | 0% |
| ether LPA 12:0 | 0.06 | 0% | |
| GP | 0.05 | 0% |
The data show that the LPA Assay has <1% cross reactivity with the lipids we have tested. Data from additional tests not shown here can be shared upon request if there are concerns about a specific lipid.
In summary, Echelon's LPA Assay is highly specific for detecting LPA, a key lipid with potential cancer biomarker applications. The extensive validation of this assay shows it can effectively distinguish LPA from similar lipids ensuring accurate LPA measurement in complex samples. The assay’s high specificity and low cross-reactivity make it a reliable tool for both research and clinical applications. For further details or specific lipid concerns, please contact us for additional information.
0.2
/ 0.3
Related Articles
Stay informed with our informative blog posts.
0.3
/ 0.3
Get in Touch
If you have any questions or would like to learn more about our services, feel free to reach out to us. We’re here to help!
Biosciences