There has been increasing interest over the last decade in harnessing RNA for novel therapuetic modalities. With the approval of the first siRNA drug in 2018 and the subsequent success of the mRNA vaccines for SARS-CoV-2, The lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems for these drugs has come into sharper focus with the approval of the first siRNA drug in 2018 and the subsequent success of the mRNA vaccines for SARS-CoV-2. Common LNP formulations contain four types of lipids, with one, the ionizable lipid, having dual packaging and release functions for the RNA cargo. However, the specific chemistry and structure of any single ionizable lipid is not broadly generalizable across applications or to individual cells and tissues. Therefore, there is a growing need for a deeper pool of these lipids to choose from as new RNA-based applications are developed.
To date, design of ionizable lipids has relied on generation of libraries via combinatorial chemistry and then high-throughput screening to identify ionizable lipids with unique properties. While these techniques are highly reliable, the time and cost associated with screening such extensive libraries can be prohibitive. These constraints also mean that some lipid components may be excluded from the design stage altogether thus limiting the structural variety of lipids that are screened. The scope of this problem is one that is uniquely suited to be addressed by deep learning algorithms.
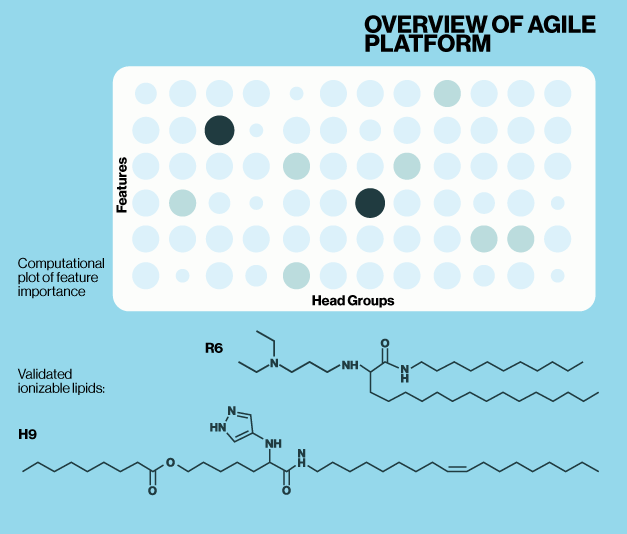
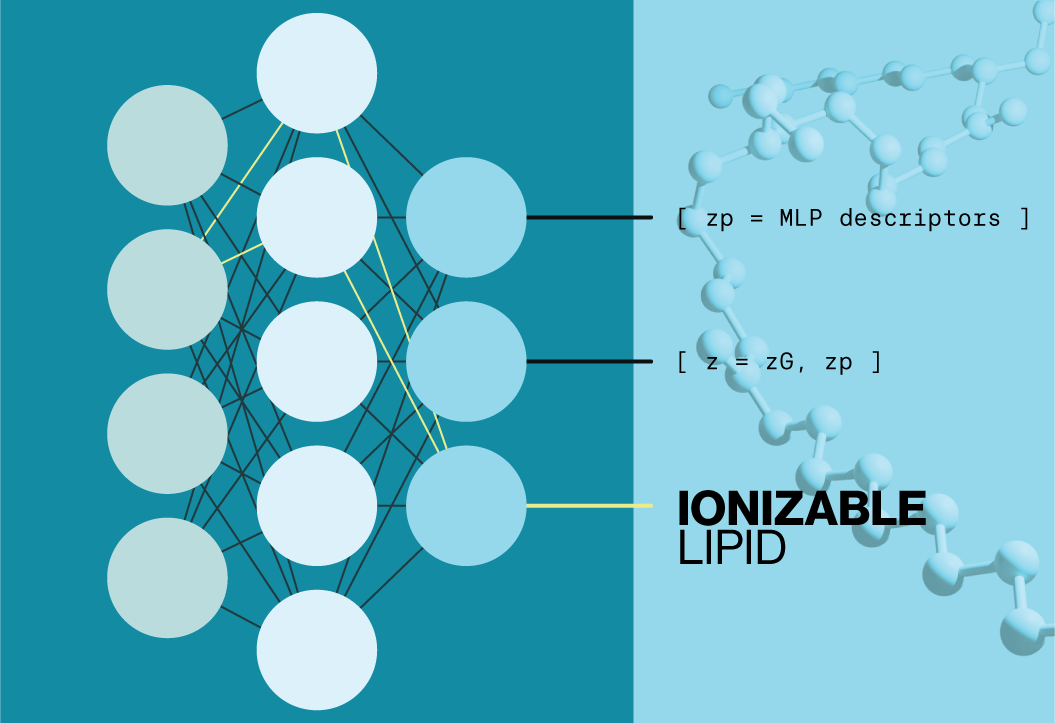
Recent work by Li and colleagues at the University of Toronto demonstrate how deep learning tools can be utilized to develop new ionizable lipids. Their platform, AI-Guided Ionizable Lipid Engineering (AGILE), utilizes structural data from libraries of small molecules and lipids which is then refined by experimental data. This parallel training enables comparison between the structures of ionizable lipids and their functional characteristics. They present evidence that their model can predict the effectiveness of novel ionizable lipids allowing researchers to design, synthesize, and evaluate ionizable lipids tailored for mRNA delivery across different cell types.
To validate the AGILE platform, novel structures were benchmarked against two well charaterized ionizable lipids, DLin-MC3-DMA and ALC-0315 (Echelon N-1020, N-1282). AGILE successfully identified two ionizable lipids, H9 and R6, with high mRNA delivery efficiency for muscle and macrophage cells, respectively. While AGILE is not a generative AI platform, the current data highlight it’s potential to rapidly identify structure-activity relationships which could dramatically reduce screening and validation time for new ionizable lipids.
Read the full article here:
AGILE platform: a deep learning powered approach to accelerate LNP development for mRNA delivery
Nature Communications (2024)
0.2
/ 0.3
Related Articles
Stay informed with our informative blog posts.
0.3
/ 0.3
Get in Touch
If you have any questions or would like to learn more about our services, feel free to reach out to us. We’re here to help!
Biosciences