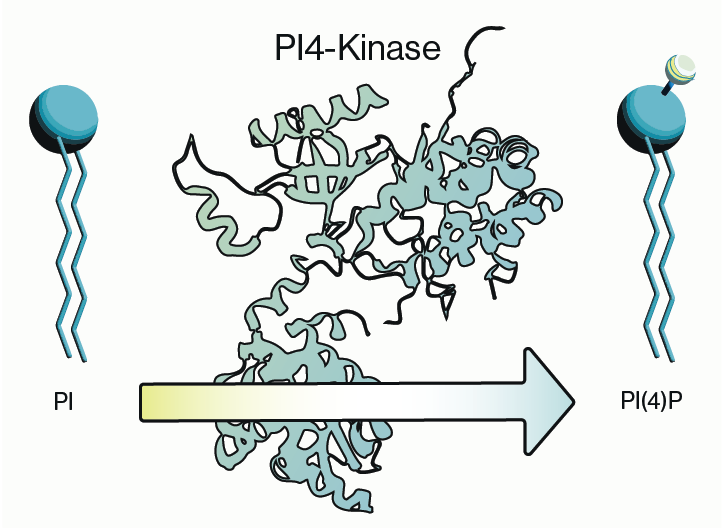
PI4-kinase, or phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase (PI4K), is an enzyme involved in the synthesis of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P), a crucial lipid signaling molecule in cells. PI4P is a precursor for phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) and therefore is involved in the regulation of membrane trafficking, including transport of vesicles containing proteins and lipids within the cell. Membrane trafficking is crucial for maintaining cell structure, communication, and various other functions. Let me break it down a bit.
PI4Ks consist of four isozymes in two subfamilies: type II kinases (PI4KIIα and PI4KIIβ) and type III kinases (PI4Kα and PI4Kβ). The structure of type II and III kinases differs significantly, which informs both their function and potential interactions with other proteins. As a result, the two types exhibit distinct modes of stimulation and inhibition.
PI4KIIα is the most abundant and active PI4K in mammalian cells and it is constitutively membrane-bound. PI4KIIα is recruited to the plasma membrane and plays diverse roles in cellular processes such as autophagy, lysosomal delivery, endosomal receptor sorting, exocytosis, signal transduction, actin remodeling, and sphingomyelin synthesis. PI4KIIβ, a less studied and less active type II PI4K, differs from PI4KIIα in its subcellular localization and activation. While PI4KIIα is constitutively membrane-bound, PI4KIIβ is mostly cytosolic or associated with various cellular compartments upon cell activation. Its recruitment to the plasma membrane upon cell activation is necessary for making it as active as PI4KIIα.
PI4Kα, a type III PI4K, has a nuclear localization sequence and pleckstrin homology domain, enabling its membrane interaction. It transiently associates with various cellular compartments, and generates a significant portion of PI4P in the plasma membrane. Type III PI4Kβ differs from PI4Kα in that it lacks a pleckstrin homology domain but possesses a region primed for post-translational modifications that modulate its activity.
PI4K in Disease
1) Neurological Disorders
PI4K has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. It plays a role in maintaining the integrity of cellular membranes, and disruptions in membrane trafficking can contribute to neurodegeneration (ND). PI4KIIα is expressed in synaptic vesicles and may play a role in some types of ND. Interactions with components of vesicle trafficking suggest potential involvement in motor disabilities that are reminiscent of other neurological disorders. Phosphorylation of PI4KIIα has also been shown to influence neuronal receptor trafficking and expression, hence PI4KIIα may be critical for proper synaptic function. PI4Kα defects are associated with neuropathy as it plays a role in myelination, and its disruption leads to severe neurodevelopmental issues. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in its promoter region is associated with schizophrenia, another neurological disorder associated with disrupted development.
2) Cancer
Altered PI4K activity has been observed in some cancer types. For example, in this recent publication, using many of the unique products we offer, they identify a potential PI4KA inhibitor and show the targeting of PI4KA can overcome chemoresistance in leukemia. Suggesting the use of PI4K inhibitors as potential anti-cancer agents.
PI4KIIα is implicated as an oncoprotein and it is highly expressed in various cancers. Loss of PI4KIIα activity drives tumor cell apoptosis through an EGFR-dependent mechanism, making it a potential therapeutic target in EGFR-dependent tumors. PI4KIIβ, strangely, appears to be antioncogenic and prooncogenic. This is likely due to the varied proteins it interacts with and individual mutations that negatively affect one binding partner but not others. In terms of expression, downregulation of PI4KIIβ in tumor cells appears to promote cancer metastasis.
Additionally, PI4Kα inhibition in brain and breast tumor cells may enhance radiosensitization and hinder growth. Despite lacking a selective inhibitor, ongoing studies aim to elucidate the crystal structure of PI4KIIβ and develop selective inhibitors due to its role in various cellular processes.
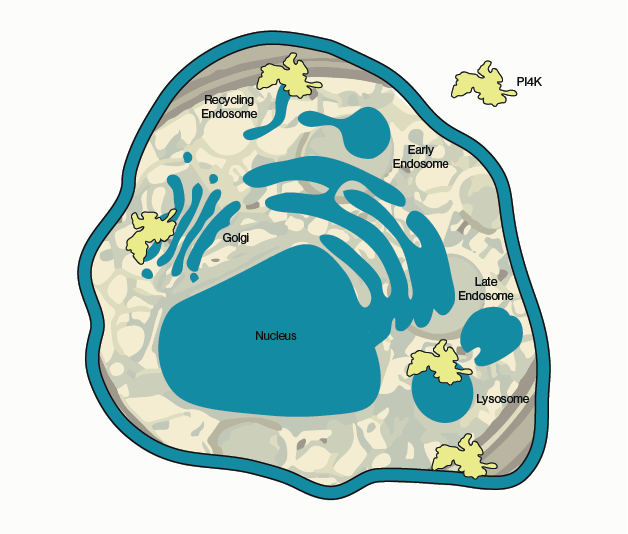
Figure 1 – Known sites of PI4K activity in the cell. Sites vary by isoform but include the Golgi apparatus, endosomes, lysosomes, and the plasma membrane.
3) Viral Infections
Certain viruses are known to hijack the host cell’s PI4K to facilitate their replication. PI4K has been shown to impair poliovirus, picornavirus, coxsackievirus replication, and HCV secretion. Most recently PI4KIIIB was implicated in SARS-COV entry via detection of PI(4)P with a PI(4)P antibody. PI4Kα is required for hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication and is recruited by NS5A viral protein for viral assembly on the plasma membrane. PI4Kα inhibitors have since been explored for potential HCV antiviral therapy.
4) Metabolic Disorders
There is emerging evidence linking PI4K to metabolic disorders such as obesity and insulin resistance. In a recent publication, using the PI4K Activity ELISA, researchers identified PI4KIIIB as a regulator of GLUT4 translocation and suggesting PI4KIIIB as a target to rescue defective glucose update in diabetics. It’s role in regulating protein translocation has also been tied to Gaucher disease, a lysosomal storage disorder that arises due to dysfunctional lipid metabolism.
Additional Notes
Research on PI4K, and its relevance to disease, is still an ongoing area of study. Currently, PI4K has been implicated in these important areas of research however, the specific mechanisms are still being actively researched. PI-273 appears to be a selective inhibitor for PI4KIIα that impedes breast cancer cell growth, reinforcing the PI4K-EGFR link for tumor targeting. Two selective PI4Kα inhibitors have been reported, but caution is advised due to potential cardiovascular issues with high doses of PI4Kα inhibition. Several selective inhibitors for PI4Kβ that target viral trafficking and replication are available, including BF738735 and enviroxime. Enviroxime previously entered clinical studies but these were discontinued, thus improved PI4Kβ inhibitors are needed.
The field of lipid signaling and its role in health and disease is complex, and ongoing studies may provide further insights into the significance of PI4K in different physiological and pathological processes. For a deeper understanding of the roles of PI4P and PI4K, I suggest this recent review.
- Jiang X, Huang X, Zheng G, Jia G, Li Z, Ding X, Lei L, Yuan L, Xu S, Gao N. Targeting PI4KA sensitizes refractory leukemia to chemotherapy by modulating the ERK/AMPK/OXPHOS axis. Theranostics. 2022 Oct 3;12(16):6972-6988. doi: 10.7150/thno.76563. PMID: 36276647; PMCID: PMC9576605.
- Yang N, Ma P, Lang J, Zhang Y, Deng J, Ju X, Zhang G, Jiang C. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIβ is required for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike-mediated cell entry. J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):8457-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.312561. Epub 2012 Jan 17. PMID: 22253445; PMCID: PMC3318727.
- Sun A, Simsek Papur O, Dirkx E, Wong L, Sips T, Wang S, Strzelecka A, Nabben M, Glatz JFC, Neumann D, Luiken JJFP. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIβ mediates contraction-induced GLUT4 translocation and shows its anti-diabetic action in cardiomyocytes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(6):2839-2856. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03669-7. Epub 2020 Oct 22. PMID: 33090289; PMCID: PMC8004495.
- Bura A, Čabrijan S, Đurić I, Bruketa T, Jurak Begonja A. A Plethora of Functions Condensed into Tiny Phospholipids: The Story of PI4P and PI(4,5)P2. Cells. 2023 May 17;12(10):1411. doi: 10.3390/cells12101411. PMID: 37408244; PMCID: PMC10216963.
0.2
/ 0.3
Related Articles
Stay informed with our informative blog posts.
0.3
/ 0.3
Get in Touch
If you have any questions or would like to learn more about our services, feel free to reach out to us. We’re here to help!
Biosciences