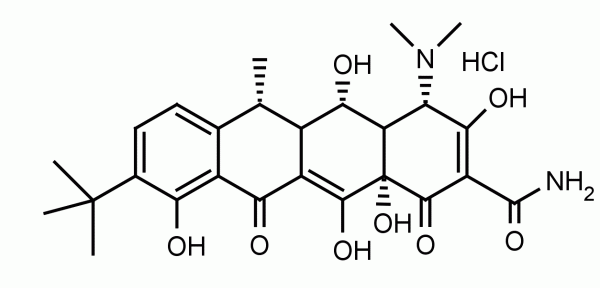
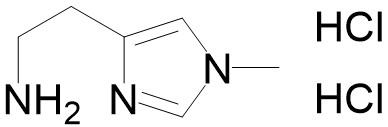
9-tert-Butyl Doxycycline (9TB) is a Tet On/Off system agonist capable of activating and acting as an inducer for the tetracycline-transactivator (tTA) and reverse tTA (rtTA), and tTA-responsive promoters (Ptets), herein known as the Tet switch. The compound is able to activate the Tet switch with approximately 10-fold greater efficacy, especially in lipophilic environments such as the brain and lung and other similar biocompartments. 9TB is freely soluble in water, and can be administered IV, IP and in the drinking water of experimental animals, allowing for ready dosing. 9TB also has found use in studying hypoxia-regulated gene expression on cell survival using the tetracycline-inducible (tet-on) system, where exposure to the inducing ligand doxycycline (dox) inhibited caspase-3 cleavage in mitochondria in
Publications
1) Zhu, P. et al., “Silencing and Un-silencing of Tetracycline-Controlled Genes in Neurons”, PLoS ONE. 2007; 2(6): e533.
2) Halterman, M.W. “An Improved Method for the Study of Apoptosis-Related Genes Using the Tet-On System” J. Biomol. Screen. 2011; 16(3): 332-337
3) Jiang, D. et al. “Airway Epithelial NF-kB Activation Promotes Mycoplasma pneumoniae Clearance in Mice” PLoS ONE. 2012; 7(12): e52969.
4) Furutachi, S. et al. “Slowly dividing neural progenitors are an embryonic origin of adult neural stem cells”, Nature Medicine, 2015; doi:10.1038/nn.3989.
5) Furlan, G., et al. (2017). “Life-Long Neurogenic Activity of Individual Neural Stem Cells and Continuous Growth Establish an Outside-In Architecture in the Teleost Pallium.” Current Biology 27(21): 3288-3301. DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2017.09.052
6) Alonso, S. B., et al. (2019). “An increase in neural stem cells and olfactory bulb adult neurogenesis improves discrimination of highly similar odorants.” The EMBO Journal 38: e98791. DOI:10.15252/embj.201798791