CAS Number: 131438-79-4
Molecular Weight: 4327.18
Salt Form: TFA
Purity: >96%
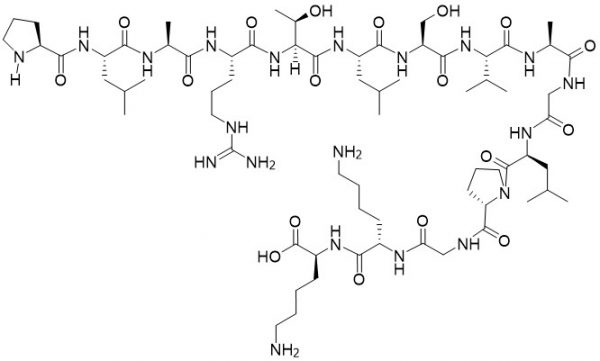
Sequence (3-letter): Asp-Ala-Glu-Phe-Arg-His-Asp-Ser-Gly-Tyr-Glu-Val-His-His-Gln-Lys-Leu-Val-Phe-Phe-Ala-Glu-Asp-Val-Gly-Ser-Asn-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ile-Ile-Gly-Leu-Met-Val-Gly-Gly-Val-Val-OH
Sequence (1-letter): DAEFRHDSGYEVHHQKLVFFAEDVGSNKGAIIGLMVGGVV-OH
Storage: -20 °C or below
Solubility: water, 1mg/ml
Beta amyloid (1-40), along with beta amyloid (1-42) (catalog # 641-15) is one of the two main variants of the amyloid β peptide involved in Alzheimer’s disease. Beta amyloid (1-40) is a peptide that is found in plaques in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and is shown to have both neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects in human and rat cell culture models.
References
1. Roher, A. et al. (1996) “Morphology and Toxicity of Ab-(1–42) Dimer Derived from Neuritic and Vascular Amyloid Deposits of Alzheimer’s Disease” J. Biol. Chem. 34: 20631–20635.
2.Tennent, G.A., Lovat, L.B. and Pepys, M.B. (1995) “Serum amyloid P component prevents proteolysis of the amyloid fibrils of Alzheimer disease and systemic amyloidosis” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 4299-4303.
3. Strittmatter, W.J. et at (1993) “Apolipoprotein E: High-avidity binding to ,B-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 1977-1981.
4. Scheuner, D. et al (1996) “Secreted amyloid bold β-protein similar to that in the senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease is increased in vivo by the presenilin 1 and 2 and APP mutations linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease” Nat. Med. 2: 864 – 870.
![641-10 Beta Amyloid [Glu11] (1-40), human (CAS 131438-79-4) - Echelon Biosciences](https://www.echelon-inc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/641-10.png)

![Angiotensin II-[Sar1], CAS 51833-69-3 - Echelon Biosciences](https://www.echelon-inc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/131-65.jpg)
![Angiotensin III, human / Angiotensin II-[Des Asp1], CAS 13602-53-4 - Echelon Biosciences](https://www.echelon-inc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/131-76.jpg)