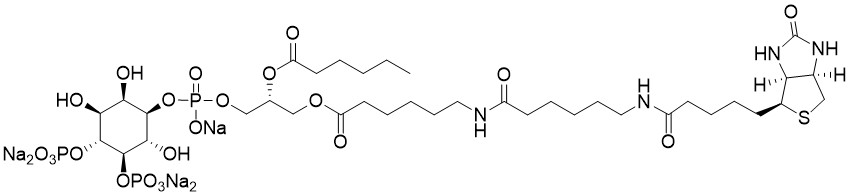
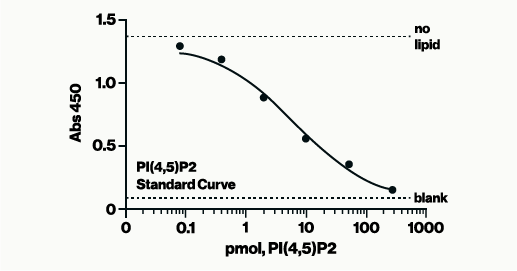
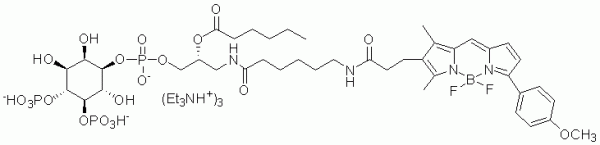
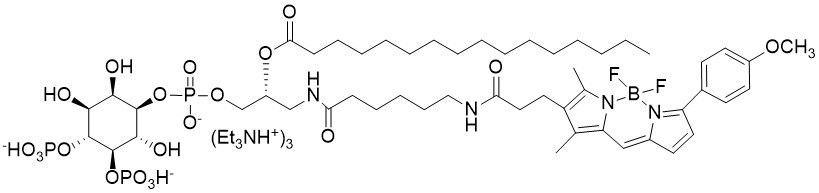
Biotin Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate is a water soluble analog of PI(4,5)P2 (PIP2) labeled with biotin at the sn-1 position.
Phosphoinositides (PIPns) are minor components of cellular membranes but are integral signaling molecules for cellular communication. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) has been shown to play a central role in a variety of cellular functions. Amongst its many functions, PIP2 is a substrate for Phospholipase C-coupled G-protein pathways involved in intracellular calcium release in a number of tissues. It is also a substrate for class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3-K) forming PI(3,4,5)P3.