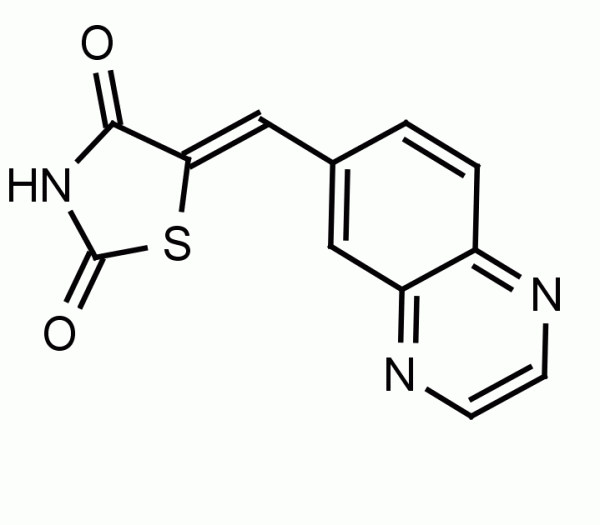
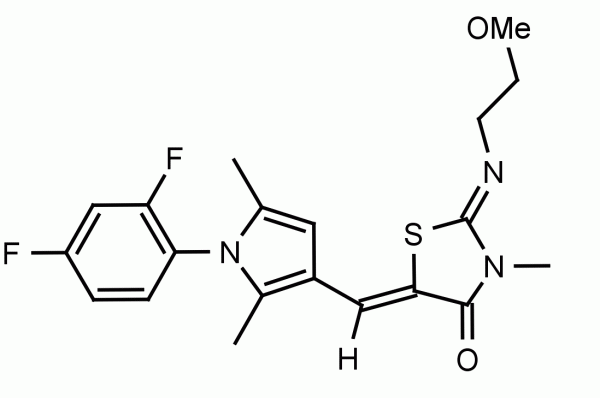
Ceramides are bioactive sphingolipids which induce apoptosis in cells. Ceramidases (CDase), which hydrolyze the fatty acid chain, keep ceramide levels in check and have been proposed as a target for small-molecule inhibitors for anti-cancer therapy. Ceranib-2 inhibits cellular CDase activity with an IC50 = 28 uM in SKOV3 cells and does not show significant cytotoxity up to 100uM. Incubations of SKOV3 cells with Ceranib-2 resulted in an increase in all ceramide species and a dose-dependant decrease in sphingosine and S1P. Ceranib-2 suppressed tumor growth in a mouse model with subcutaneous JC cell tumors.
References
1) J.M Draper, et al. “Discovery and Evaluation of Inhibitors of Human Ceramidase” Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2052-2061
2) H.S. Vethakanraj, et al. “Targeting ceramide metabolic pathway induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines” Biophys. Biochem. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 833-839.
![Benzo[a]pyrene - Echelon Biosciences](https://www.echelon-inc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/1452.gif)