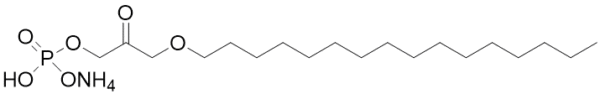
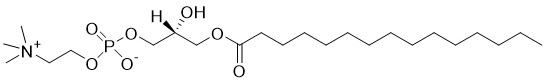
Hexadecyl dihydroxyacetone phosphate, ammonium salt, (Hexadecyl-DHAP) is an ether lipid implicated in membrane function and is involved in lipid biosynthesis.
Ether lipids have been implicated in cell membrane function and can act as signaling molecules; however, their roles in cell physiology are still not completely understood. The key step for ether lipid biosynthesis is the conversion of acyldihydroxyacetone phosphate (acyl-DHAP) to alkyldihydroxyacetone phosphate (alkyl-DHAP) by the enzyme alkyldihydroxyacetone phosphate synthase (ADPS, alternately referred to as AGPS). Recently, elevated levels of ADPS have been found in human cancer cells and primary tumors which lead to increased levels of oncogenic signaling lipids.