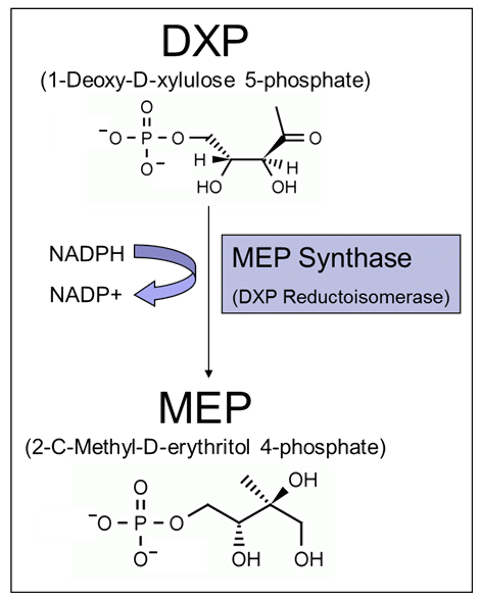
The MEP Synthase (DXR) Enzyme Inhibitor Screen evaluates compounds for inhibition of DXR activity. This medium throughput inhibitor screen provides a valuable tool for the identification of potential antimicrobials, specifically inhibitors of the MEP Synthase (DXR) enzyme in the MEP pathway.
Sample Type: Compounds for inhibition of DXR activity
Assay sensitivity: IC50 of Fosmidomycin ~ 130 nM (Fosmidomycin is supplied as a control inhibitor.)
Assay Incubation time: Ten minutes (Continuous Kinetic Readout)
Sample Considerations: Run compounds in ≤ 5% overall DMSO concentration
Echelon’s MEP Synthase (DXR) Enzyme Inhibitor Screen will evaluate compounds for inhibition of DXR activity. The assay monitors the depletion of β-NADPH which corresponds with the conversion of the DXP substrate to the MEP product. The MEP pathway is used by most bacteria, including all Gram-negative bacteria, for isoprenoid biosynthesis.
Isoprenoids are made from two main building blocks: isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). The MEP pathway is one of two ways to produce these isoprenoid building blocks and is found in most bacteria and plant chloroplasts. The other pathway, the mevalonate (MVA) pathway is mainly present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some Gram-positive bacteria. Due to this natural distribution, the MEP pathway makes a good target for new antibiotics and herbicides. Fosmidomycin, a natural product inhibitor of MEP Synthase, has confirmed the pathway’s potential as a target for antibiotics.
Keywords: Methylerythritol Phosphate Pathway, MEP Pathway, antibacterial, non-mevalonate pathway, MEP, Methylerythritol Phosphate, Isoprenoid biosynthesis, Isoprenoid, DXP, MEP Synthase, IspC, 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate, 1-Deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate, Deoxyxylulose phosphate, DOXP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritrol, Fosmidomycin, MEP Pathway Inhibitor Screen