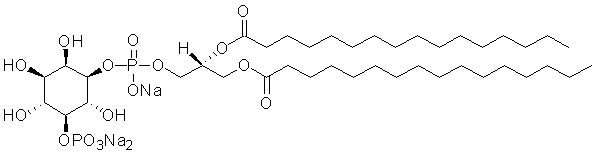
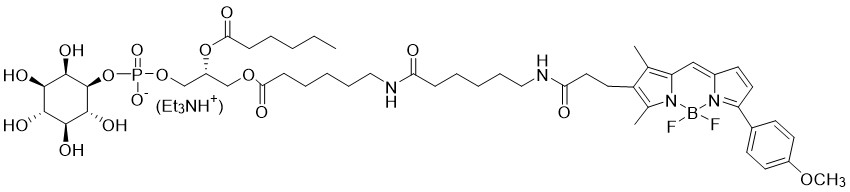
Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate diC16 (PI(5)P diC16) is a synthetic, purified dipalmitoyl PI(5)P.
Phosphoinositides (PIPns) are minor components of cellular membranes but are integral signaling molecules for cellular communication. Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate (PI(5)P) is a rare lipid found in the nucleus that can bind the PHD finger of the nuclear adapter protein ING2. PI(5)P is phosphorylated to PI(4,5)P2 by Type II PIP kinases.
Alternate Names: D-myo-Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, Dipalmitoyl Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, PtdIns(5)P C16, PI(5)P C16, or PI5P
Bulk discounts available, please email echelon@echelon-inc.com for information.
Publications
1) Barylko, B., S. H. Gerber, et al. (2001). “A Novel Family of Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinases Conserved from Yeast to Humans.” J Biol Chem 276(11): 7705-7708.
2) Sbrissa, D., O. C. Ikonomov, et al. (2004). “Role for a Novel Signaling Intermediate, Phosphatidylinositol 5-Phosphate, in Insulin-Regulated F-Actin Stress Fiber Breakdown and GLUT4 Translocation.” Endocrinology 145(11): 4853-4865.
3) Grainger, D., C. Tavelis, et al. (2011). “Involvement of phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in the L6 myotube model of skeletal muscle.” Pflugers Archiv European Journal of Physiology 462(5): 723-732.
4) Bua, D.J., Martin, G.M. et al. (2013). “Nuclear phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate regulates ING2 stability at discrete chromatin targets in response to DNA damage.” Sci. Rep.3: 2137.
5) Sumita, K., Y.-H. Lo, et al. (2016). “The Lipid Kinase PI5P4Kb Is an Intracellular GTP Sensor for Metabolism and Tumorigenesis.” Molecular Cell. DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.12.011